Views: 6
A new article published in Physical Review D showcases the remarkable contribution of AstroCeNT researchers Theo Hugues (Group 1) and Masato Kimura (Group 4) as part of the DarkSide-50 collaboration.
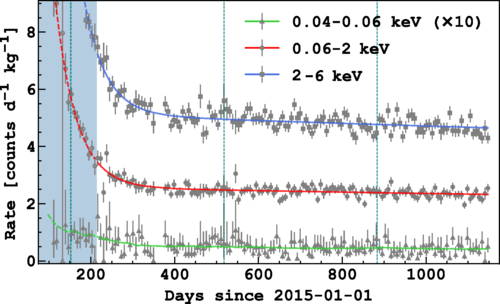
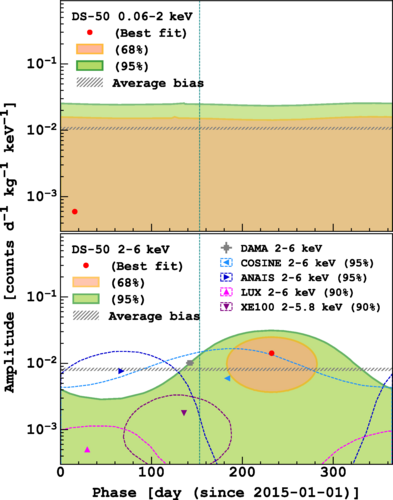
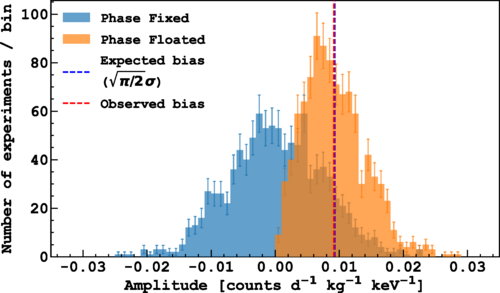
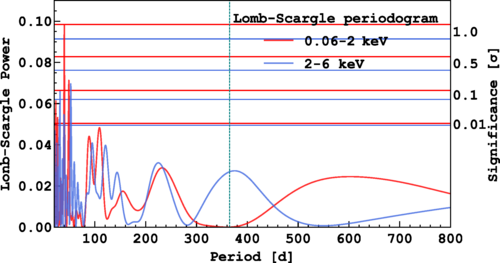
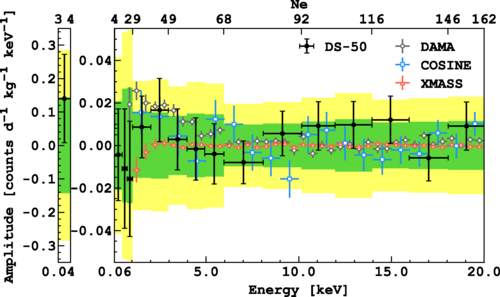
The study explores the possibility of detecting dark matter through its predicted annual modulation effect caused by the Earth’s motion around the Sun. Using the advanced liquid argon time projection chamber at DarkSide-50, the team set a new benchmark for sensitivity, achieving the lowest energy threshold (40 eVee) ever in such a search. Although no significant modulation signature was observed, this work represents a important step forward in the quest to unravel the mystery of dark matter.
DarkWave’s funding has been instrumental in supporting these researchers, enabling their contributions to cutting-edge science.